Nanocomposites replace animal tissue in new valve design
Researchers at UBC have created the first-ever nanocomposite biomaterial heart-valve developed to reduce or eliminate complications related to heart transplants.
By using a newly developed technique, the researchers were able to build a more durable valve that enables the heart to adapt faster and more seamlessly.
Assistant Professor Hadi Mohammadi runs the Heart Valve Performance Laboratory (HVPL) through UBC Okanagan’s School of Engineering. Lead author on the study, he says the newly developed valve is an example of a transcatheter heart valve, a promising new branch of cardiology. These valves are unique because they can be inserted into a patient through small incisions rather than opening a patient’s chest—a procedure that is generally safer and much less invasive.
“Existing transcatheter heart valves are made of animal tissues, most often the pericardium membrane from a cow’s heart, and have had only moderate success to date,” explains Mohammadi. “The problem is that they face significant implantation risks and can lead to coronary obstruction and acute kidney injury.”
The new valve solves that problem by using naturally derived nanocomposites—a material assembled with a variety of very small components—including gels, vinyl and cellulose. The combination of their new material with the non-invasive nature of transcatheter heart valves makes this new design very promising for use with high-risk patients, according to Mohammadi.
“Not only is the material important but the design and construction of our valve means that it lowers stress on the valve by as much as 40 per cent compared to valves currently available,” says Dylan Goode, a graduate researcher at the HVPL. “It is uniquely manufactured in one continuous form, so it gains strength and flexibility to withstand the circulatory complications that can arise following transplantation.”
Working with researchers from Kelowna General Hospital and Western University, the valve will now undergo vigorous testing to perfect its material composition and design. The testing will include human heart simulators and large animal in-vivo studies. If successful, the valve will then proceed to clinical patient testing.
“This has the potential to become the new standard in heart valve replacement and to provide a safer, longer-term solution for many patients.”
The new design was highlighted in a paper published this month in the Journal of Engineering in Medicine with financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
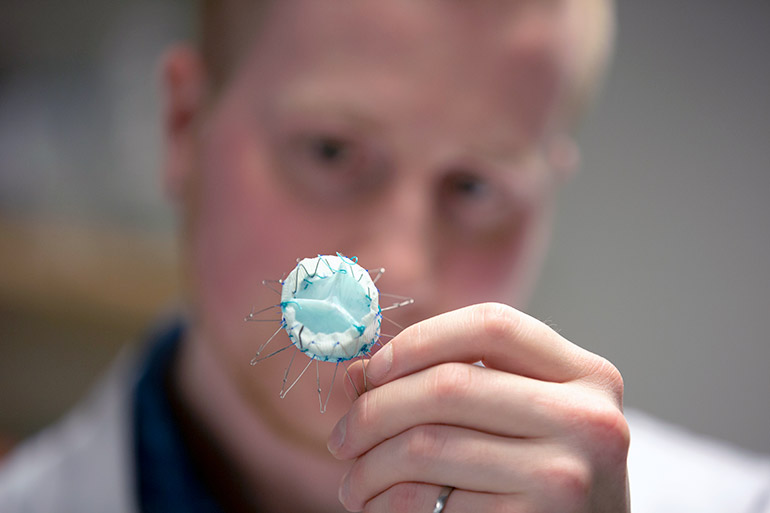
By using a newly developed technique, UBC researchers were able to build a more durable valve that enables the heart to adapt faster and more seamlessly after a transplant.
About UBC’s Okanagan campus
UBC’s Okanagan campus is an innovative hub for research and learning in the heart of British Columbia’s stunning Okanagan Valley. Ranked among the top 20 public universities in the world, UBC is home to bold thinking and discoveries that make a difference. Established in 2005, the Okanagan campus combines a globally recognized UBC education with a tight-knit and entrepreneurial community that welcomes students and faculty from around the world.
To find out more, visit: ok.ubc.ca.